6 Stages of Software Development Life Cycle
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) or app-development life cycle is a process to build a software methodologically. It consists of six different stages all of which are important in itself. In order to build a good software, it is imperative to follow the software development life cycle step by step. The software life cycle falls into 6 levels starting from requirements gathering and ending in the maintenance phase. If you want to come up with satisfactory results, it is essential to follow all these different stages of the software development life cycle.
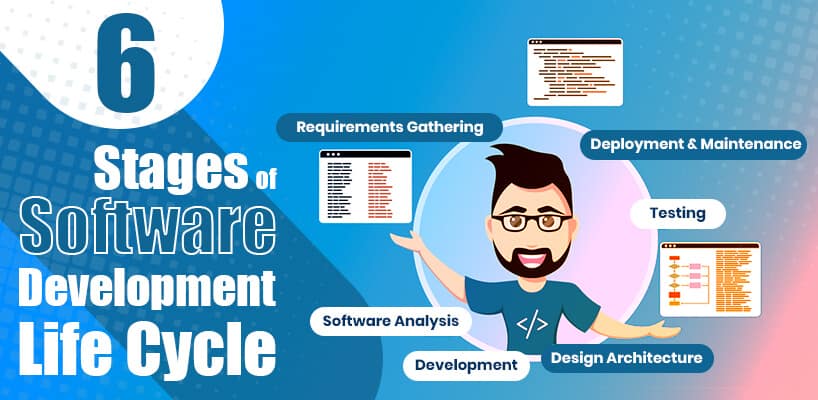
6 Stages of Software Development Life Cycle
- Requirements Gathering
- Software Analysis
- Design Architecture
- Development
- Testing
- Deployment and Maintenance
Phase 1: Requirements Gathering
Requirements gathering is the first most crucial phase of the software development life cycle. It decides how your software will look and perform at the end. To build a quality software, it is imperative to spend ample time in this phase. During this step, the project managers or business analyst meet with the customer and ask for the software specifications. It happens during communication, business meetings or during interviews with customers. Therefore, it is recommended to ask open-ended questions to pull out the maximum details of the project. The more information you gathered, the more it will become easy to understand client expectations from the project.
Here are some key points you must not forget while working in phase 1:
Know the target audience and purpose of the Software: Knowing the purpose of the software will open out the details why software is required and who will be the users of the software. The target audience will help you to build the software from their perspective and enables you to get the results as expected.
Identify the Problem: Most of the software are built to address some specific problems. Like Uber was initiated considering the transport hurdles in San Francisco. It is good to explore the problem first then leverage technological advancement to solve the issue.
Phase 2: Software Analysis
Once you are done with the requirements gathering, you need to draw the project timeline and scope. Not only this, but the second phase also helps you to explore the functional and non-functional requirements of the project.
Software Analysis is the process of collating factual data, identify software flaws, understanding the information architecture and developing solutions to overcome the weaknesses of the project. In the end, a software requirement specification (SRS) is built which determines the overall cost. It also defines the functionalities which will be designed and developed during the project lifecycle.
Phase 3: Design Architecture
When you have the SRS in your hand, then it’s the time to move on to phase 3. In this phase, you design the architecture of the software. Considering technical requirements you can propose one or more than one design approach and document it in a DDS (Design Document Specification). There are two types of design; high-level design and low-level design. High-Level Design is the overall software design covering the system architecture and database design. It helps you to understand the flow of the system. Whereas, the low-level design is the extension of HLD. Class diagrams and entity relationship diagrams all comes under LLD, and it covers all the programs specifications.
When the DDS is built, the stakeholders review it and based on the reviews the best approach is selected. The selected approach is then modified with the feedback.
Phase 3 identifies the design architecture of the project and all the functional and non-functional requirements of the project. It is the best phase to correct your mistakes in case you find any or else your time and cost will get doubled.
Phase 4: Development
This phase requires developers to implement what has been decided in the previous phases. The developers build the code, test, integrate and manage. It is the longest phase of SDLC because all the development takes place in this phase. As the life cycle is divided into manageable pieces, it needs to be accomplished step by step. The implementation in this phase depends on the development model you choose for your project.
Phase 5: Testing
Testing is the crucial phase of the software development life cycle. It helps to find the bugs and errors of the software. There are four different types of testing; unit testing, integration testing, acceptance testing and system testing. The testing team test each project module and check either they are functioning properly. After passing through the various testing stages, the software is ready to go live.
Phase 6: Deployment and Maintenance
In this stage, the software is released in the market. Sometimes, the project is released to the current clients only and based on their feedback changes are made. After the project is released successfully in the market, maintenance is carried out for customers. The project team updates software to make sure it is relevant to the current market needs.
Benefits of SDLC
Following the software development process can allow to control and manage the software on a high level. You can not only save the project from failure but can also correct the flaws in the mid stages. All the team members are assigned their duties, software development cost is finalized and risks are identified.
More About SDLC
If you are following the software development life cycle you should also know its different models that are:
Waterfall Model: In the waterfall model, steps are followed logically. You need to complete the previous phase first then you can move on to the next phase. It is the straightforward and oldest SDLC model.
Agile Model: The Agile model breaks the project into the cycle. It divides the module and the working model is released fairly quickly. Every module is sent to the client for feedback and then, at last, all the modules are summed to develop the final end-product.
Iterative Model: The iterative model is based on the concept of repetition. The software is developed quickly at a low cost. Then onwards it is tested and improve through rapid and successive versions.
V-Shaped Model: The V-shaped model is also followed logically like the waterfall model. The only difference is that every development stage is tested as it is completed.
Big Bang Model: The Big Bang model does not follow any planning or process. It is ideal for small projects and can be started with little cost.
Spiral Model: The spiral model is the amalgamation of the iterative model with the controlled aspects of the waterfall model. It follows incremental releases of the product through each iteration around the spiral.
As the technology is evolving in the digital world today, humans are becoming dependent for their needs. Now, there are not only social apps that are making communication easy but also the apps to manage daily routine chores.
Therefore, it has become important to adopt the emerging trends. It will help you to stay ahead in the competition.
Code Creators is a leading IT company in Canada who offers custom software development services at an affordable price. If you have any app idea in your mind and want us to be your service provider, you can contact us via live chat or email.


